GLOSSARY
What Is Open Source Intelligence: The Importance of OSINT in Your Organization’s Threat Landscape
In order to gain the upper hand, security strategies must include a diverse means of gathering intelligence, both for a predictive and reactive approach. Open-source intelligence has become crucial to completing this picture
Introduction to Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
A modern security professional’s job is becoming more and more complex. It’s no surprise considering the influx of unexpected places where threats are beginning to surface. In order to gain the upper hand, your security strategy must include a diverse means of gathering intelligence, both for a predictive and reactive approach. In an era where content is being created at an exponential rate – 90% of the world’s data was created in the last 2 years alone – the future of security must be intelligence-led.
A major source of intelligence that cannot be overlooked is the vast amount of publicly available information (PAI) being produced by consumers, hackers, newsmakers, and bloggers every single day. Globally, almost every person and organization is communicating across multiple platforms and networks, as well as handling personal and corporate needs virtually – such as shopping, travel planning, and data management. Finding like-minded communities and audiences online is the goal. However, wherever you have people congregating, especially if there is potential for monetary gain, the risk of nefarious behavior rises. This has created an increased need for open-source intelligence (OSINT) and OSINT platforms.
What is Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)?
Open-source intelligence, or OSINT, refers to the process of gathering information from public, legal data sources to serve a specific function. Some open sources might include social media, blogs, news, and the dark web.
The concept of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) very basically works like this:
Public information exists → data is gathered → information is analyzed for intelligence.
The purpose of seeking information from public data varies on the type of insights you wish to gather. Many industries and professionals look to open sources to uncover workplace security threats, protect executives, prevent loss, manage assets, gauge brand sentiment, and monitor conversations for creating marketing strategies. Intelligence professionals use certain types of OSINT and OSINT platforms for investigations, prosecution, evidence gathering, and events monitoring.
What is finished intelligence?
Finished intelligence, or ‘cooked’ data, is raw data that has undergone processing to gain context and become actionable. The collection, processing, and analysis of raw data are foundational steps along the threat intelligence lifecycle.
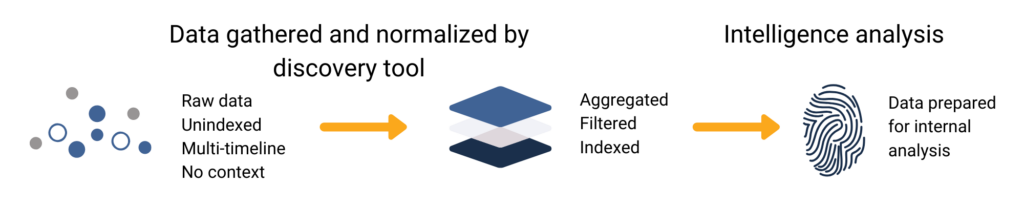
Raw data is unaltered from its original source. This could look like a network’s traffic data logs, dark web discussions, or even public social media posts.
Finished intelligence would look like a report summarizing the context interpreted from relevant raw data points and suggested security responses.
Finished intelligence services allow organizations to skip the raw data collection and analysis steps, which are time-consuming and require skilled analysts. Those steps are instead supported by automation and machine learning capabilities, and/or third-party analyst teams.
The main goal of finished intelligence is to operationalize the process so organizations can respond faster to active threats and invest less time and resources in gathering and contextualizing large volumes of raw data. The result is a finished intelligence report that the client can immediately act on. While expensive, finished intelligence solutions can be ideal for private sector organizations seeking a “comprehensive” security solution.
What can OSINT tools do?
OSINT tools can identify and separate entities within a data set (parsing), and organize and display those entities by category to glean meaning and avoid redundancies (normalizing). OSINT tools can also index raw data so that it’s quickly and easily searchable and filtered for relevancy.
Access to publicly available online data is often free, but the true value lies in what can be analyzed and extracted from the data. Organizations using OSINT for security and intelligence require the ability to detect key information quickly and efficiently. They can do so by using robust OSINT tools.
The vast amount of online data is overwhelming to sift through, and with the complex ways today’s online threat actors conduct themselves, the vulnerabilities to organizations are becoming more elusive. Open-source data, when gathered, enriched, and monitored effectively, can be extremely valuable for predicting, analyzing, and reviewing incidents at every stage of their occurrence. But where to begin?
Suggested Reading: The Five Phases of the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
Where to look for publicly available information
Where you look for information depends on what you want to find. Running a Google search is a simple form of OSINT, but when you are responsible for the safety and security of a particular person, place, or asset, you need to be casting a keen eye over multiple sources. Criminal behavior tends to be hidden, and it is unlikely a surface web search will take you there.
What threats can OSINT help with?
The emergence of intelligence-led security is a direct result of the varied and growing range of on-the-ground threats that are being plotted, planned, discussed, and executed online. As our physical and digital realities are becoming more and more interlaced, individuals and organizations are creating more informational weaknesses and thereby more opportunities for an ever-widening range of attacks and other threats to occur.
These threats include:
- Hacking
- Information leaks
- Extremist activity
- Geopolitical threats
- Fraud
- Violent attacks
- Disinformation campaigns
OSINT tools can be invaluable for handling internal processes such as:
- Brand protection
- Workplace and facilities safety issues
- Real-time event monitoring
- Executive protection and force protection
- Natural disasters and incident response
OSINT for enterprise security
Global enterprises are operating in the age of digital transformation. This has plenty of benefits for companies, helping improve customer experience, productivity, and resource management. But along with these benefits, wider technology adoption also means increasing opportunities for compromise.
This stands true for almost any industry with an online presence—including finance, retail, and transportation, which make up some of the world’s most cyber-targeted industries. Digital transformation also affects physical security and cyber-enabled threats as criminals adopt anonymized online communication channels. What do these risks look like?
Cyber threats
- Data breaches targeting corporate and customer information
- Phishing, business email compromise (BEC), and other forms of impersonation
- Malware and ransomware attacks
- Credential stuffing
- SIM swapping
- Distributed denial of services (DDoS) attacks
- Zero-day exploits
Cyber-enabled threats
- Credit card fraud
- Money laundering
- Counterfeiting
- Theft and gift card fraud
- Workplace harassment
- Insider threats
Physical security threats
- VIP-targeted doxxing and harassment
- Travel risk management
- Event monitoring
- Crises like terrorism and natural disasters
OSINT tools support enterprise security teams in identifying and responding to these risks. Social media networks provide real-time updates from on-the-ground threats near executives and other physical assets like offices, employees, and corporate events. Paste sites, forums, and marketplaces across the deep and dark web often publish the earliest indicators of data breaches and executive-targeted doxxing. Anonymized discussions on these covert sites help security teams identify fraud, insider threats, and cyber-attack strategies directly from the source.
Combined with other risk management feeds and tools, OSINT platforms provide security teams with more context and earlier risk indicators so they can respond faster and avoid blind spots.
But many organizations face challenges in responding to risk quickly and effectively, especially as more enterprise teams—from marketing to IT and compliance—require OSINT.
According to a 2021 report by Forrester Research, 42% of corporate decision-makers are currently improvising when it comes to risk management. Almost 70% claim that risk information is siloed across their departments and only 29% are confident in their risk management technologies.
What do security teams need from OSINT platforms to address information gaps?
- Broad data coverage
There are thousands of different online sources out there, from social media platforms to the deep and dark web, where relevant risk data is hiding. Many risk management tools focus only on one data source type—such as social media or the dark web—to help security teams find relevant risk information. A more ideal solution combines a variety of these sources within one platform so teams don’t have to juggle more tools than are necessary. This can just lead to information gaps and slower responses.
- Simplicity and usability
Not everyone who needs access to online risk data has a technical background. OSINT solutions should be accessible to anyone in an organization without the click-heavy processes and complex interfaces that are typical of IT-based risk management software. Personnel should be able to easily and quickly separate the most pertinent data and view it in a digestible format.
- Speed-to-information
OSINT tools that prioritize real-time data allow security teams to get critical insights faster. This gives organizations a much better chance of avoiding or mitigating threats from all angles.
- Collaboration features
For risks where cross-department visibility is necessary, OSINT solutions should offer permission settings and collaboration features that allow teams to view each other’s activities or tackle a security threat together when there is overlap.
Integrations
Many global organizations already have a suite of risk management tools. OSINT solutions should be able to easily integrate with third-party solutions, whether they include a UI or funnel data directly into existing systems.
OSINT for national security: What national security initiatives does OSINT support?
- Counter-terrorism and counter extremism
Foreign jihadist groups like the Islamic State and Al-Qaeda are no longer solely responsible for the threat of terrorism and extremism. Domestic extremist movements based on conspiracy theories, right-wing ideology, and discriminatory worldviews now also pose serious national security threats. Public online spaces play a huge role in spreading propaganda, recruiting, financing, and planning. This data helps governments understand how extremist groups operate so they can then predict public safety risks and protect citizens and assets from domestic and global terrorism.
- Addressing misinformation and disinformation
National security threats have expanded to include online influence campaigns, which can compromise democratic processes and lead to real-world security risks. Disinformation (which is engineered to deliberately deceive) and misinformation (false information that is not necessarily spread with malicious intent) is widely prevalent online. Monitoring online spaces is crucial for tracking disinformation campaigns so governments can mitigate their impact and keep the public safer and more informed.
- Cybersecurity
Breaching government data is financially and politically lucrative for lone-wolf attackers, organized hacking groups, and advanced persistent threat groups. Sophisticated technologies are available to a greater diversity of adversaries than ever before. Persistent online threats include breaches and cyber espionage targeting classified data, network attacks disrupting critical infrastructure, and botnets enabling malware attacks and information warfare. Paste sites, discussion forums, and marketplaces on the deep and dark web often provide early indicators of breaches, malware, and attack techniques. Combining this open-source data with other cybersecurity feeds helps intelligence teams more confidently predict, mitigate, and investigate cyber compromise.
- Transportation security
National transportation networks, including airports, seaports, and highways, make up a country’s critical infrastructure. When this infrastructure is compromised, governments and security teams need to stay prepared and alerted to prevent damage to assets, data, and human life. Online data plays a crucial role in providing the intelligence required for informed transportation security planning and incident response. For intelligence teams, social media networks and deep and dark web content can:
- Provide the earliest alerts for location-based threats near airports, seaports, and other transportation hubs
- Inform security teams about tactics used to bypass security systems or commit attacks, particularly at airports
- Monitor for threats directly targeted at the security/public sector organizations themselves
- Stay alert to vulnerable data that could compromise a transportation network’s digital or physical security
- Addressing national and global crises
When a national crisis occurs, governments must make timely, informed decisions to protect their data, assets, and citizens. As we’ve seen with the COVID-19 pandemic, adversaries co-opt real-world events in their strategies. Whether it’s a natural disaster, public health crisis, or terrorist attack, intelligence teams need to know how and where the crisis is occurring and how to allocate response resources. Online spaces are often the earliest sources of information to provide this context—for example, social media users often post public updates and images from the scene of a crisis. Aligning this data with other feeds can help provide a faster and more informed response.
Intelligence professionals require specialized software to collect this information and generate actionable intelligence. Commercial OSINT tools help intelligence teams gather open-source data more efficiently and align with a team’s unique requirements. Because intelligence teams often work with their own interfaces and tooling, they often require direct access to raw data that can be plugged into their existing systems.
How do OSINT platforms address data overload?
The intelligence community is increasingly challenged by growing volumes of online data available for collection, processing, analysis, and triage. The western world is also facing a data analyst shortage coupled with a growing demand for military AI. As a result, data scientists in the public sector tend to handle more complex tasks, developing tooling and data sets to support lower-level analysts on intuitive platforms.
Intelligence teams are also challenged by a lack of access to some emerging online sources. For example, fringe networks (like alt-tech platforms, deep and dark web imageboards and paste sites, etc.) do not offer their own API or are unavailable through commercial API providers. To gather data from these sources, analysts are often required to create dummy accounts, make group requests, and navigate networks manually. This requires a significant amount of HUMINT resources that could be allocated to other areas of the intelligence cycle.
To address these challenges, Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) tools must:
- Improve data coverage by providing access to relevant sources, including fringe web spaces, that are not commonly available through commercial, off-the-shelf vendors.
- Leverage machine learning capabilities. AI is a major priority for governments, helping analysts process and contextualize intelligence more efficiently.
- Be intuitive and user-friendly for lower-level intelligence analysts, providing more efficient workflows and better speed-to-information.
Types of OSINT tools
There are many types of OSINT tools on the market, both free and paid. The truth is, no single OSINT tool is 100% effective as a standalone solution. Rather, combining a variety of solutions is the best practice. Remember that the best OSINT tools will have a geographical element, providing a digital window to view data by location. The tools you choose will depend on the specific needs of your organization. Here are some types of OSINT tools to consider:
Social media monitoring
Our OSINT Platform allows organizations to use online information to gain situational awareness on the ground. Security teams utilize predictive intelligence and real-time crisis management, as well as brand monitoring and post-incident review.
Deep and dark web monitoring
The Flashpoint product suite includes targeted, automated collection systems that capture information from the deep and dark web, enabling your security and intelligence teams to identify and prioritize relevant threats and leverage their intelligence to act quickly.
Email hacks
Have I Been Pwned? is a free online resource to check if your email address has been put at risk due to a data breach.
Twitter monitoring
TweetDeck allows you to view multiple timelines in one user view. TweetDeck allows a user to create specific filters such as specific activity and geographical locations.
Internet archives
Wayback Machine is an internet archive tool, like a library, of historical data. This tool allows the user to search the history of archived websites, metadata, text contents, and TV news captions.
Link analysis
Maltego is a graphical link analysis tool that accelerates and simplifies complex investigations by allowing users to build visualizations and connections between disparate data sets.
Conclusion
Business is happening online, and today’s security strategies need to be informed by the masses of social data being created every day. Gathering, filtering, and analyzing this information requires the advanced capabilities of OSINT platforms.
Both amateur and professional criminals are using sophisticated strategies and seemingly innocuous networks to conduct illicit business. More and more media networks are being infiltrated and used outside their intended purposes. Evolving threats require predictive and intelligence-led security strategies. Security teams must gather intelligence from every corner that they can. Open source threat intelligence software is essential for any enterprise using public data sources to inform their decision-making.
Not only can OSINT help protect against hidden intentional attacks such as information leaks, theft, and fraud, but it also has the ability to gain real-time and location-based situational awareness to help protect people at work, at events, institutions, or even the shopping mall. The right OSINT toolkit will give your security and intelligence teams the upper hand.
Get the latest news and insights delivered to your inbox.
Interested to see top news from Flashpoint hit your inbox directly? Subscribe to our newsletter to receive curated content on a regular basis.

